The infamous Lazarus Group is holding strong. They show no signs of slowing down. According to a new report, the sophisticated hackers, connected with the North Korean Government, have left behind evidence.
Methods of Operation
Earlier this month, an unnamed blockchain technology company was hacked by the Lazarus Group. This time, it was a systems administrator who fell for a phishing scam by giving up their LinkedIn password to bad actors.
The hackers were able to manipulate registry keys and gain access to the firm’s computers. Security firm F-Secure detailed the methods the hackers used in the attack and shared the results with the public.
The new F-Secure report uses intelligence gathered from various recent attacks to paint a picture of the Lazarus Group. The report identifies a certain pattern they say can help businesses protect themselves from further attacks.
Analysis of the attack found similarities in malware Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures (TTPs), and intelligence related to other attacks. The research matches details published by other security firms like Kaspersky and ESET.
The criminal group leverages spear-phishing attacks, custom malware, and native operating systems (OS) to reach its objectives. These techniques are sophisticated.
They require in-depth research and customization. Such attacks require patience and coordination. This makes them more dangerous but requires good organization, which sets Lazarus apart from other hackers.
Evidence
Though the Lazarus Group has not claimed ownership of many attacks, there appears good evidence that they were carried out by the same group.
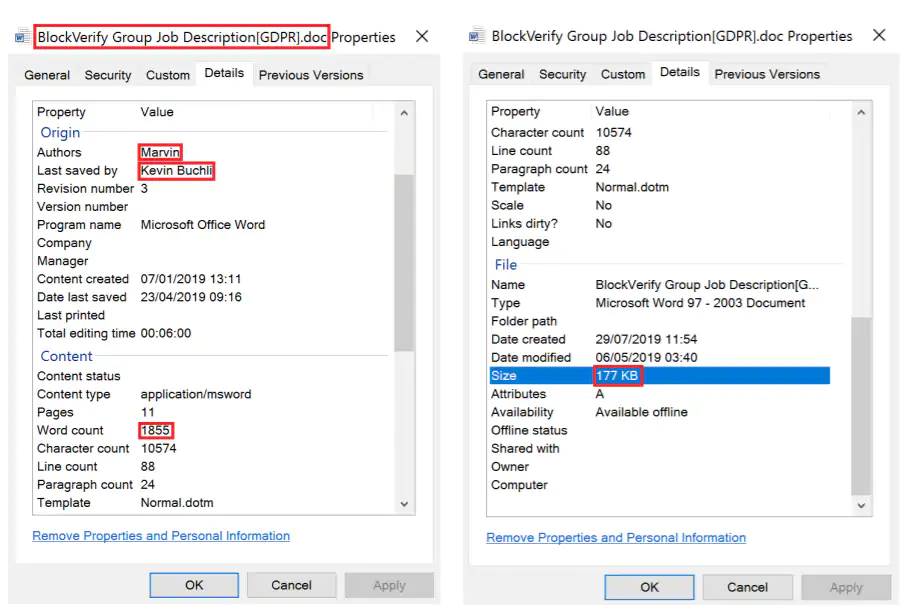
The paper demonstrates consistent markers throughout the attacks. For example, certain author names in the metadata of malware files appear the same. Some files also have identical save dates and total file sizes. This suggests that they all came from the same source.
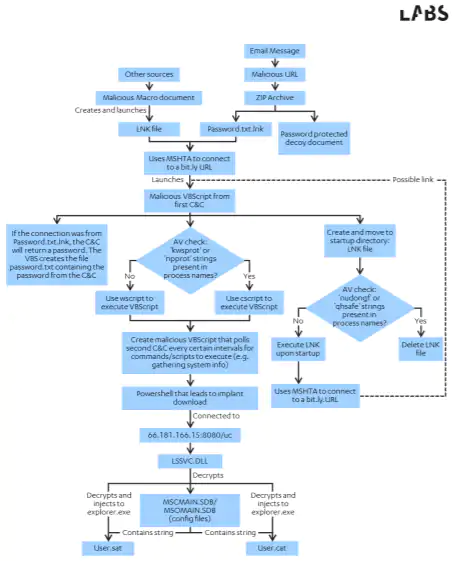
What’s more, F-secure found similarities in the “chain of infection” the malware took. In other words, the sequence of files that became infected to ultimately take over the computer was very similar.
Hiding in Plain Sight
Interestingly, the Lazarus Group, though thorough, left behind a trail of bread crumbs. In analyzing command line sequences, F-Secure found that some commands in the code were ‘hidden’ from plain sight. They said,
Throughout F-Secure’s investigation it became evident that Lazarus Group was conscious to avoid detection and would remove evidence of their presence.
However, the Lazarus Group did not remove all traces of wrongdoing. The hackers took down anti-malware software using easily identifiable and unique commands.
This left the researchers with a calling card with which to identify the Lazarus Group. It’s F-Secure’s hope that by identifying these commands, companies will be able to prevent future attacks.
Despite the fact that the Lazarus Group attacks were detectable, F-Secure also concluded that their methods were changing over time. Said simply, the hackers are learning from their mistakes. The firm is thought to be operating since at least 2017 and remains concentrated on the lucrative cryptocurrency industry.
A separate though similar attack occurred when a teenage hacker used spear phishing to access several high profile Twitter accounts last month.
Earlier this year, the US Treasury Department sanctioned two Chinese nationals in connection with a Lazarus Group malware attack on an Indian power plant.



 BlocksInform
BlocksInform










