Can crypto reach 1 billion users by 2025?
The cryptography industry could reach up to 1.2 billion people by 2025, although it is growing at the most conservative pace.

 BlocksInform
BlocksInform

Bitcoin and other risk assets are under pressure in the short term as macroeconomic discourse switches from recession to sticky, anchored inflation.
The markets are poised for impending recession. However, the current macroeconomic analysis suggests that perhaps there will be no recession, at least not in the short term. Rather, analysts are anticipating a period of persistent and well-anchored inflation.
On Feb. 24, the U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) released Personal Consumption Expenditure (PCE) data for January, showing an actual rate of 4.7%, much higher than the expected rate of 4.3%.
PCE measures the price of goods and services, similar to the Consumer Price Index (CPI), but differs by sourcing data from businesses as opposed to consumers, as is the case with CPI.
Differs by whether the data comes from businesses or consumers, as is the case for the CPI.
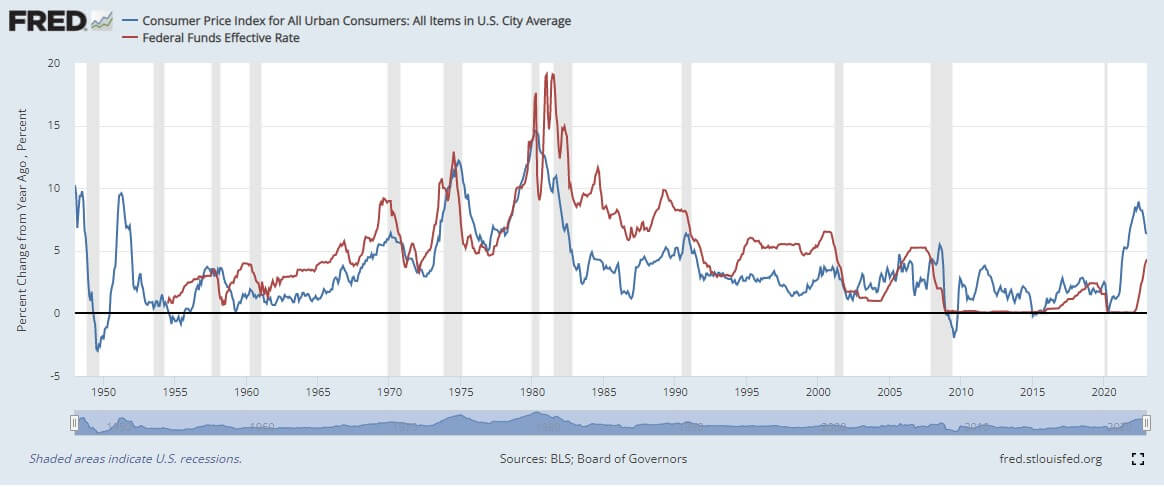
The upshot of this is likely further hawkishness from the Fed, which stated that its primary goal is to bring inflation down to 2%.
In turn, whether higher inflation would become the prevailing discourse, The effect might be the price pressure on Bitcoin, and other risky properties, as disposable income dwindles to keep up with the cost of essential commodities.
Fed funds futures data previously pointed to growing confidence within the interbank lending market. But recent movements demonstrate that this narrative has changed.
Fed funds futures refer to derivatives based on the federal funds rate – the lending rate charged by banks (to other banks) for overnight lending.
The graph below shows that federal funds forward contracts for September 2023, December 2023 and December 2024 have increased. A higher rate appears to indicate that banks do not trust other banks, which means that interbank borrowing becomes more costly.
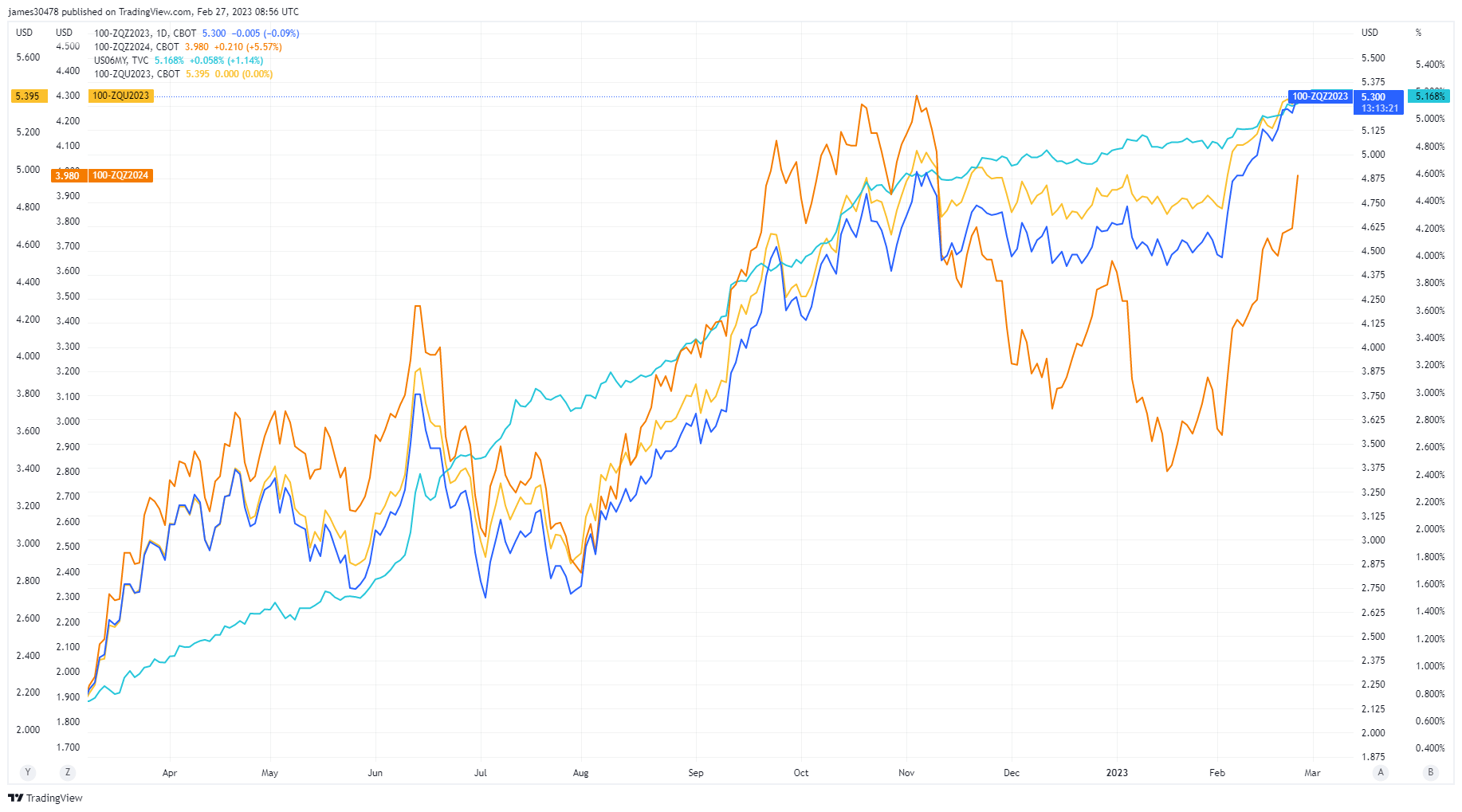
Source: TradingView.com
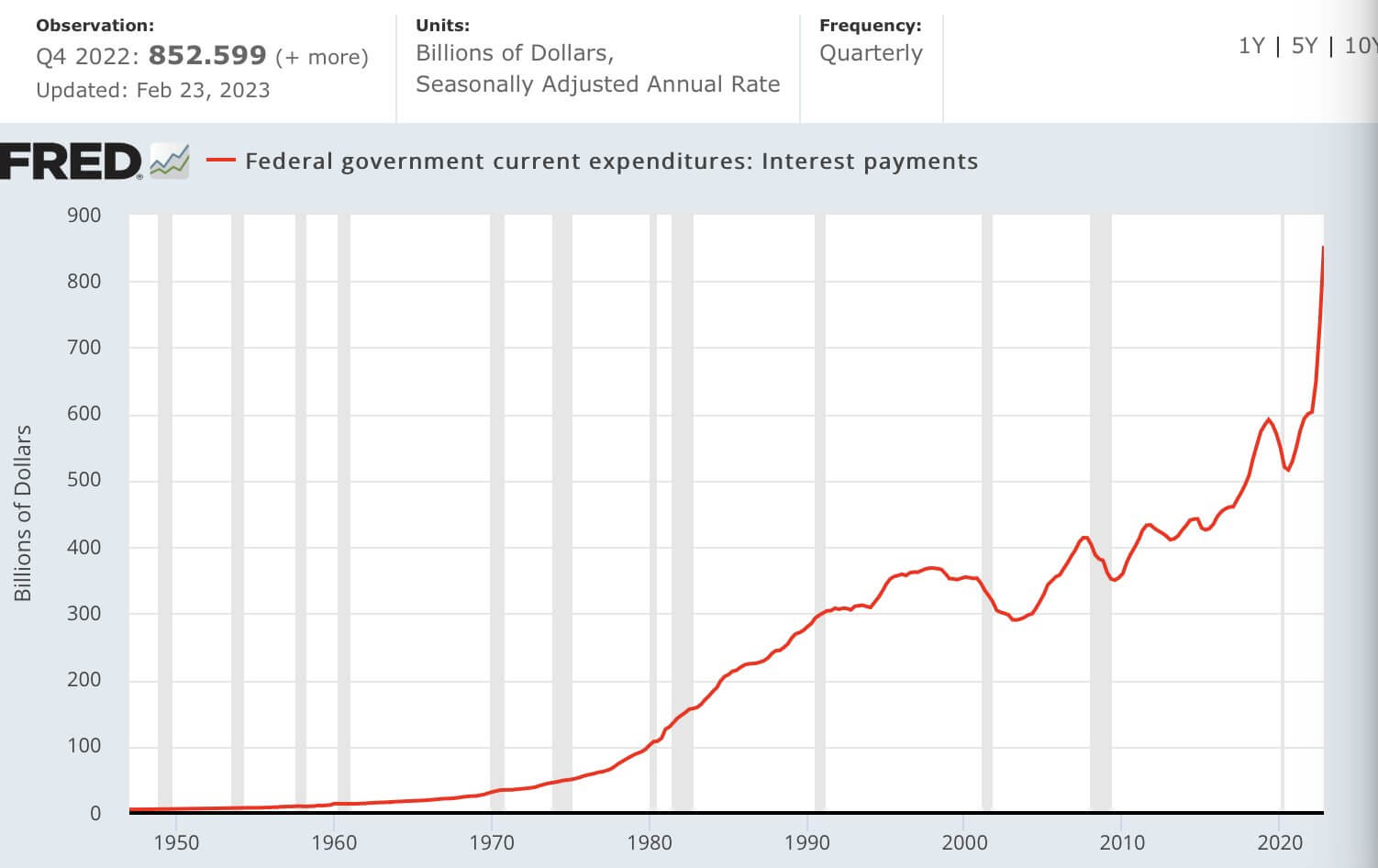
Maintain higher rates over time. The graph below illustrates that interest payments have nearly doubled since 2020.
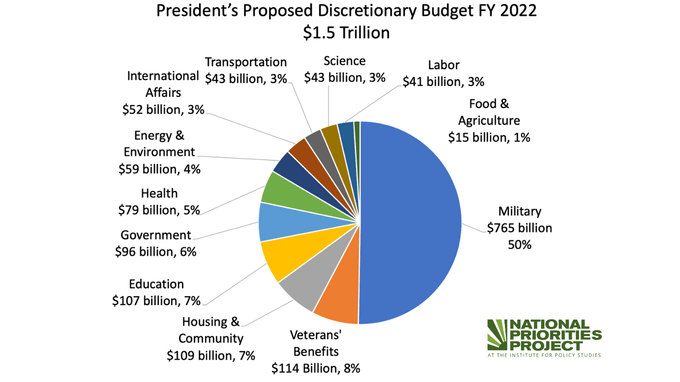
50% of 2022’s $1.5 trillion discretionary budget was spent on the military, with the next most significant slice, at 8%, allocated to Veterans’ Benefits totaling $115 billion.
Longer-term maintenance of interest rates would make servicing the existing debt more difficult – This places the Federal Reserve in a difficult position in terms of achieving an inflation rate of 2 per cent.
The updated predicted terminal interest rate now comes in at 5.25% -5.50%, giving leeway of 75 basis points from the current rate.
The next meeting of the Committee is planned for March 22nd. At the moment, economists are 70% in favour of an increase of 25 basis points, with the remaining 30% expecting an increase of 50 basis points.
At the moment, economists are 70% in favour of an increase of 25 basis points, with the remaining 30% expecting an increase of 50 basis points.
The cryptography industry could reach up to 1.2 billion people by 2025, although it is growing at the most conservative pace.
