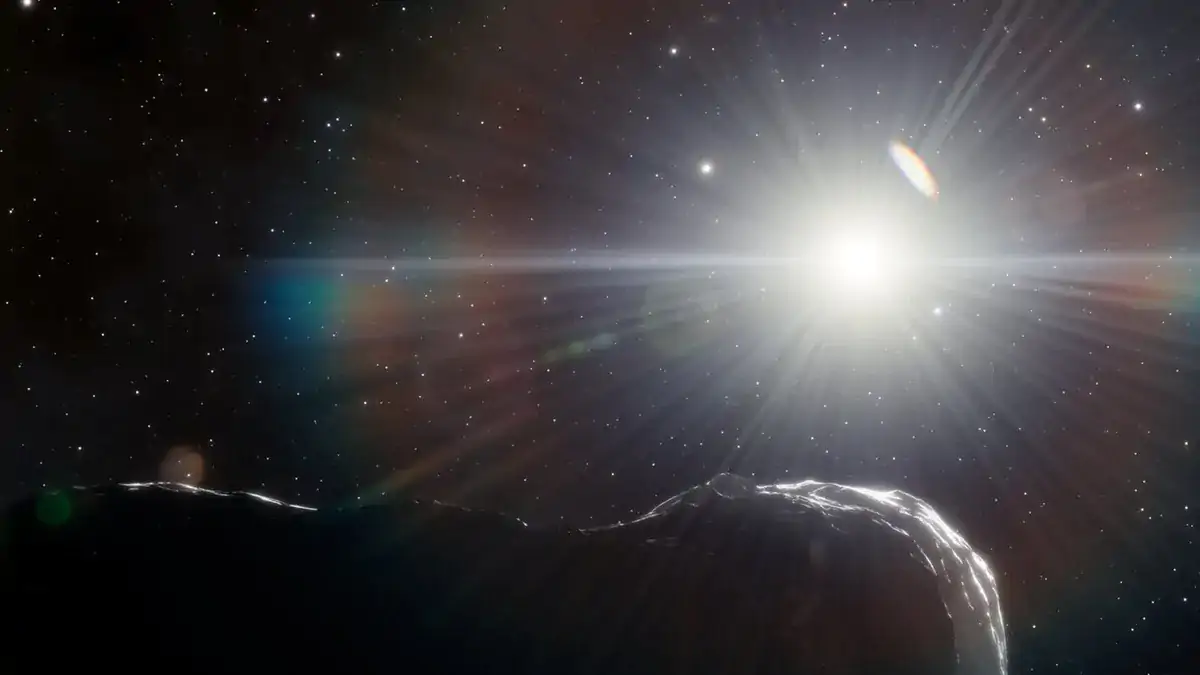
An international team of astronomers has found three asteroids close to the Earth (neas) hiding in the inner solar system, safely hidden in the sunlight. One of them is a huge asteroid, nicknamed a "planet killer" who might one day collide with the earth.
One does not have to worry, as currently there are no predicted approaches with the Earth.
Named ap7 in 2022, the 0.9 mile wide (1.5 kilometre) asteroid is the largest potentially dangerous object to the Earth that has been found in the last eight years. The trio of asteroids remains unnoticed until now while hiding inside the orbits of Earth and Venus, wrapped in the blinding light of the sun. Astronomers only have two short 10-minute windows every night to keep an eye on the area. The challenges do not stop at the glare of the sun; they must look across a rather thick layer of the earth's atmosphere. It may skew their comments.
Asteroid hunters therefore had to wait until the conditions of observation favorable to the twilight to locate the space rocks.
"There are likely only a few NEAs with similar sizes left to find, and these large undiscovered asteroids likely have orbits that keep them interior to the orbits of Earth and Venus most of the time," Scott S. Sheppard, an astronomer at the Earth and Planets Laboratory of the Carnegie Institution for Science and the lead author of the paper describing this work, said in a statement. "Only about 25 asteroids with orbits completely within Earth’s orbit have been discovered to date because of the difficulty of observing near the glare of the Sun,"
The astronomers detailed their work in The Astronomical Journal.
The Dark Energy Camera was instrumental in the discovery of the three asteroids.
The finding was made possible, thanks to the U.S Department of Energy-fabricated Dark Energy Camera located on the Victor M. Blanco 4-meter Telescope at Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory in Chile, a Program of NSF's NOIRLab.
The black energy camera, or decam, includes high-performance broad-field CCD imagers, which can capture details of the sky with "high sensitivity".
'Large areas of the sky are required because internal asteroids are few and far between, And deep images are necessary as the asteroids are weak and you fight the bright twilight sky close to the sun as well as Earth's atmosphere distorts," said Sheppard. " DECam can cover great areas of the sky at depths impossible to reach with small telescopes, giving us a chance to go deeper, sky over, and survey the indoor solar system in a new way."
The discovery also included two other asteroids called 2021 LJ4 and 2021 PH27, that have orbits that safely remain completely interior to Earth’s orbit. 2021 ph27 is especially interesting since this is the asteroid closest to the sun. Therefore, it has the greatest "general relativity effects of all objects in and around our solar system, its surface becomes warm enough to melt the lead," according to the press release.
'Our decam study is one of the most important and sensitive research ever carried out on objects in Earth's orbit and close to Venus' orbit,' said Sheppard. "It's a once-in-a-lifetime chance to figure out what kinds of objects are hidden in the inner solar system."
This research is especially important for the identification and comprehension of the "distribution" of small bodies in the solar system. Because asteroids distant from the sun are easy to detect, they tend to dominate existing theoretical models of spatial rocks.
Study Abstract:
We are conducting a survey using twilight time on the Dark Energy Camera with the Blanco 4 m telescope in Chile to look for objects interior to Earth's and Venus' orbits. So far, we have found two rare atira/apohele asteroids, 2021 lj4 and 2021 ph27, which have orbits entirely inside the orbit of the earth. We also discovered a new object close to earth (neo) of the apollo type that crosses the Earth's orbit, 2022 ap7. Two of them have diameters?1 km. 2022 ap7 is probably the biggest potentially dangerous asteroid (pha) found in approximately eight years. To this day, we have covered 624 square degrees of sky close to and within Venus' orbit. The mean images go to 21.3 mag in the band r, with the best images about 22e mag. Our new finding 2021 ph27 possesses the smallest semimajor axis known for an asteroid, 0.4617 au, and the most important general relativist effects (53 arcs/century) known to any body of the solar system. The investigation detected? Fifteen percent of all known atira neos. We impose heavy stresses on any stable population of co-orbital resonance objects of existing venus, as well as on the atira and vatira classes of asteroids. These populations of internal asteroids are important to complete the census of asteroids near the Earth, including some of the most likely terrestrial impactors which cannot be readily discovered in other surveys. Comparing the actual population of asteroids found interior to Earth and Venus with those predicted to exist by extrapolating from the known population exterior to Earth is important to better understand the origin, composition, NEO and its population structure.




 BlocksInform
BlocksInform